Mgcl2 agno3 agcl mg no3 2 – Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of chemistry as we explore the intriguing interactions between MgCl2 and AgNO3. This exploration will shed light on the formation of AgCl and Mg(NO3)2, delve into the solubility characteristics of these compounds, and unveil their diverse properties and applications.
Prepare to be enthralled as we unravel the intricate tapestry of chemical reactions, solubility, properties, and applications that define MgCl2 and AgNO3.
Chemical Reactions: Mgcl2 Agno3 Agcl Mg No3 2
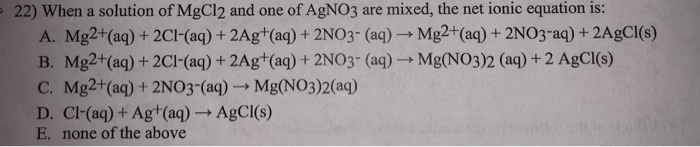
When MgCl2 and AgNO3 are mixed in an aqueous solution, a chemical reaction takes place. This reaction results in the formation of AgCl and Mg(NO3)2.
Formation of AgCl and Mg(NO3)2
The reaction between MgCl2 and AgNO3 can be represented by the following chemical equation:
MgCl2(aq) + 2AgNO3(aq) → 2AgCl(s) + Mg(NO3)2(aq)
In this reaction, the magnesium (Mg) ions in MgCl2 are replaced by silver (Ag) ions from AgNO3. This results in the formation of solid silver chloride (AgCl) and aqueous magnesium nitrate (Mg(NO3)2).
Solubility
Solubility refers to the ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent, forming a homogeneous mixture. In this context, we will explore the solubility of magnesium chloride (MgCl 2) and silver chloride (AgCl) in water.
Factors Affecting Solubility, Mgcl2 agno3 agcl mg no3 2
The solubility of a compound is influenced by several factors, including temperature, solvent nature, and the presence of other solutes.
- Temperature:Generally, the solubility of most ionic compounds, including MgCl 2and AgCl, increases with increasing temperature. As temperature rises, the solvent molecules gain more kinetic energy, allowing them to break apart the solute particles more effectively, leading to increased solubility.
If you’re curious about the chemical reactions involving MgCl2, AgNO3, AgCl, and Mg(NO3)2, you might also be interested in exploring the concept of trapezoids. Given ABCD is a trapezoid , you can delve into its properties and relationships with other geometric shapes.
Returning to our chemical equations, we can further investigate the precipitation reactions and solubility rules governing these compounds.
- Solvent Nature:The nature of the solvent also plays a role in solubility. Polar solvents, such as water, are more likely to dissolve ionic compounds like MgCl 2and AgCl because they can interact with the charged ions through dipole-ion interactions.
- Presence of Other Solutes:The presence of other solutes can affect the solubility of a compound. The common ion effect states that the solubility of a compound decreases when a common ion is added to the solution. For example, adding chloride ions to a solution containing AgCl will decrease the solubility of AgCl.
Properties
Magnesium chloride (MgCl2) and silver nitrate (AgNO3) are ionic compounds with distinct physical and chemical properties. Let’s delve into their properties and compare their similarities and differences.
Physical Properties
- Appearance:MgCl2 is a white, crystalline solid, while AgNO3 is a colorless, crystalline solid.
- Solubility:Both compounds are highly soluble in water. MgCl2 dissolves readily in water, forming a colorless solution. AgNO3 also dissolves easily in water, producing a colorless solution.
- Melting point:MgCl2 has a relatively low melting point of 714 °C (1317 °F), while AgNO3 has a higher melting point of 212 °C (414 °F).
- Boiling point:MgCl2 boils at 1412 °C (2574 °F), while AgNO3 boils at 452 °C (846 °F).
Chemical Properties
- Reactivity:MgCl2 is a relatively inert compound, while AgNO3 is more reactive. AgNO3 is a strong oxidizing agent and can react with reducing agents, such as metals, to form silver metal.
- Hygroscopicity:MgCl2 is hygroscopic, meaning it absorbs moisture from the air. AgNO3 is not hygroscopic.
- Acidity/Basicity:MgCl2 forms a neutral solution in water, while AgNO3 forms a slightly acidic solution.
Comparison of Properties
MgCl2 and AgNO3 share some similarities, such as being crystalline solids and highly soluble in water. However, they differ in their reactivity, hygroscopicity, and acidity/basicity. MgCl2 is less reactive and hygroscopic than AgNO3, and it forms a neutral solution in water, while AgNO3 forms a slightly acidic solution.
Applications
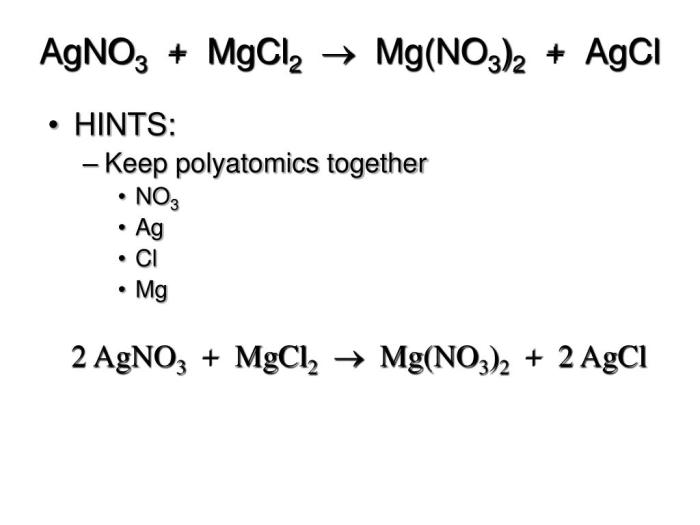
Magnesium chloride (MgCl2) and silver nitrate (AgNO3) are versatile compounds with numerous applications across various industries.
Magnesium Chloride (MgCl2)
- Road Deicing:MgCl2 is widely used as a road deicing agent, effectively melting ice and snow on roads and sidewalks. It is less corrosive to vehicles and infrastructure compared to other deicing salts.
- Magnesium Production:MgCl2 is a key raw material in the production of magnesium metal, which is used in lightweight alloys for aerospace, automotive, and construction industries.
- Textile Industry:MgCl2 is used in the production of fire-resistant fabrics and as a sizing agent for textiles.
- Pharmaceuticals:MgCl2 is used as a magnesium supplement in medications and as a laxative.
- Agriculture:MgCl2 is used as a fertilizer to supply magnesium to plants.
Silver Nitrate (AgNO3)
- Photography:AgNO3 is used in traditional photography as a light-sensitive material in photographic emulsions.
- Jewelry:AgNO3 is used in the electroplating process to coat jewelry and other metal objects with silver.
- Medicine:AgNO3 has antibacterial and antifungal properties and is used as an antiseptic and cauterizing agent.
- Water Treatment:AgNO3 is used as a disinfectant in water treatment systems to kill bacteria.
- Electronics:AgNO3 is used in the production of conductive silver pastes and electrodes.
These applications highlight the importance of MgCl2 and AgNO3 in various industries, contributing to safety, production efficiency, and technological advancements.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the chemical equation for the reaction between MgCl2 and AgNO3?
MgCl2 + 2AgNO3 → 2AgCl + Mg(NO3)2
Is MgCl2 soluble in water?
Yes, MgCl2 is highly soluble in water.
What are the physical properties of MgCl2?
MgCl2 is a white, crystalline solid with a melting point of 714°C and a boiling point of 1412°C.
What is a common application of AgNO3?
AgNO3 is commonly used in photography as a light-sensitive material.